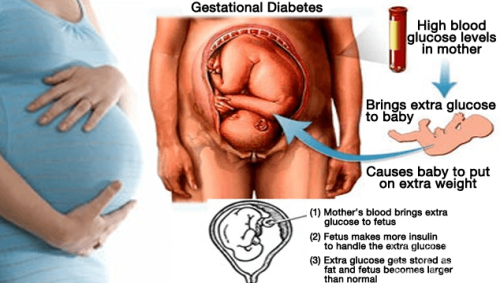
Gestational Diabetes is a very rare form of diabetes which occurs exclusively in pregnant women during the gestational period of the fetus [5]. Similar to the other forms of diabetes, Gestational Diabetes also results in the cells of the body being unable to effectively absorb blood sugar, leading to a higher concentration of glucose in the blood.

Resistance to insulin is a normal physiological response during pregnancy induced by the maternal hormones released by the mother’s body. However, in some cases, this resistance becomes high enough to result in high levels of blood sugar, enough to be classified and diagnosed as Gestational Diabetes. In such women, the pancreas is not able to produce enough insulin to overcome the insulin resistance.
Gestational Diabetes may be defined as hyperglycemia with its first presentation or onset during pregnancy. About 2-6% women suffer from gestational diabetes. The disease proves to affect both the mother and the child and can also cause major complications at the time of delivery of the child.
Usually, after the delivery of a child, the blood sugar levels of the mother return down to normal, but both the mother as well as the child are at a risk of developing Type II Diabetes later on in the future. As such, Gestational Diabetes is not by itself a chronic condition, but it exposes individuals to the risk of developing chronic diabetes later on in life.
While Gestational Diabetes is a serious pregnancy complication that must be dealt with seriously, it can easily be controlled by a combination of a healthy diet, sufficient exercise and also medication in some cases.
Pathology of Gestational Diabetes
The exact cause of Gestational Diabetes is still unknown and researchers still debate on the possible causes as to why some particular women stand a higher risk of developing the disorder than other women. However, the way in which a woman’s body behaves in this condition is fairly well-known and agreed upon.
During pregnancy, the insulin sensitivity falls in the mothers and this subsequently increases the blood glucose levels to provide adequate nutrition to the fetus. The Human placental lactogen hormone, also known as Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin reduces the insulin sensitivity in mothers. It also alters the metabolism of fatty tissues in pregnant women, releasing fatty acids as an alternate energy source for the mother, freeing up glucose for the fetus.
The mothers who face a greater risk of developing Gestational Diabetes are those who:
- Are older than 35 years of age when pregnant
- Have a history of any type of diabetes in first degree family members
- Have had a baby that had a birth defect or weighed more than 9 pounds
- Are hypertensive in nature
- Have excess amniotic fluid in the body, a condition known as polyhydramnios
- Have had a history of stillbirth or an unexplained miscarriage in the past
- Were overweight before their pregnancy with a body mass index (BMI) of more than 30
Just like Type II Diabetes, even Gestational Diabetes occurs due to inadequate insulin secretion as well as decreased responsiveness to insulin. In most of the cases of gestational diabetes, it is corrected after the delivery but in some cases it may continue to occur. Gestational diabetes is harmful to both mother and fetus and may result in few complications if not controlled.
The placenta connects the blood supply of the mother to the blood supply of the developing fetus and it allows hormones to also pass through. Thus, the abnormality caused by Gestational Diabetes also passes on to the child’s blood stream and this can trigger very harmful conditions. The high concentration of blood sugar can allow the baby to grow to a much larger size than normal and one of the most common complications associated with child birth in mothers with Gestational Diabetes is the requirement of delivery of the baby through a C-Section surgery operation. This procedure is recommended if the baby grows to more than 9 pounds in weight and such procedures are also carried out much in advance to the expected delivery date of the child.
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
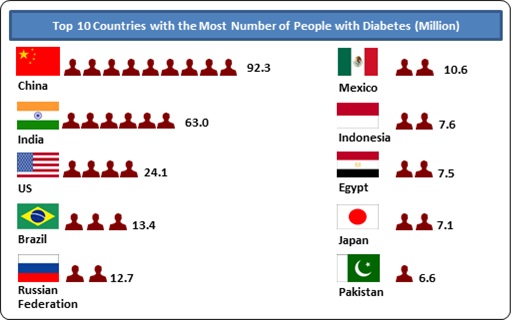
Usually the symptoms of Gestational Diabetes are mild and are not life-threatening. Some of the common symptoms are:
- Blurred vision
- Increased thirst
- Increased urination
- Increase in appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Frequent infections
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight loss
Gestational Diabetes may cause the mother to develop a condition known as preeclampsia. Preeclampsia is a very serious complication associated with Gestational Diabetes which proves to be life threatening to both the mother and the developing fetus.
Another one of the major and common complications that may be encountered with Gestational Diabetes is that the increased blood glucose levels may enter into the fetus’ blood leading to macrosomia or large sized baby which may further lead to difficulty in delivering the child via the birth canal. This also raises the chances of a C-section birth rather than a normal birth.
Gestational Diabetes also raises the risk of an early labor and associated complications, which includes babies born with a respiratory distress syndrome. Such affected babies require assistance with breathing until the lungs are capable of functioning properly on their own.
The babies that are born out of a mother with high blood sugar levels may suffer from low blood sugar levels in their body after birth as their body’s production of insulin is much higher than normal. This condition, known as hypoglycemia, if left unattended, may even result in seizures and other complications in the baby.
Both the mother and the child that are affected by Gestational Diabetes also face a high risk of developing Type II Diabetes later on in life.
Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes
There are several different types of screening tests that are used in order to diagnose Gestational Diabetes [1].
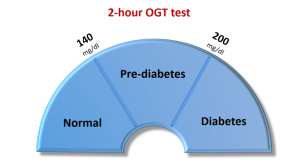
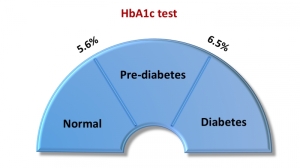
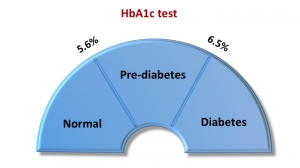
Since Gestational Diabetes develops in third trimester of pregnancy, thus the women should be screened for diabetes by Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) between 24th-28thweek. OGTT measures the ability of the body to use glucose.
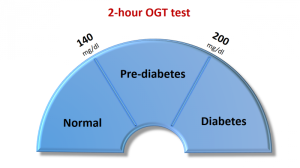
The World Health Organization (WHO) proposes using a 2-hour 75g OGTT, with a threshold plasma glucose concentration of greater than 7.8 mmol /L (140 mg/ dL) at 120 minutes as screening for gestational diabetes.
 |
 |
These days a simple glucometer may be used at home to measure the blood glucose level themselves by the mothers. There are various tests for monitoring the well-being of fetus like the non-stress test.
Some of the routine tests that are typically carried out include the glucose challenge test to the mothers which is then followed by a glucose tolerance test in order to diagnose the disorder in pregnant women.
Women who have been diagnosed with the disorder will require very frequent medical check-ups and these are to be even more followed during the final three months of pregnancy. The pregnant women will also need to actively monitor as also manage their high blood sugar levels, in conjunction to the medical check-ups. The condition can lead to very serious complications for both the mother and the developing fetus if left unattended.
Post the delivery of the child, usually the blood sugar levels in the mother fall down back to normal. However, all mothers who have suffered from Gestational Diabetes will require medical check-ups every now and again. The glucose levels of the blood will also need to be monitored as the mother is at a high risk of developing Type II Diabetes later on in the future.
Treatment of Gestational Diabetes
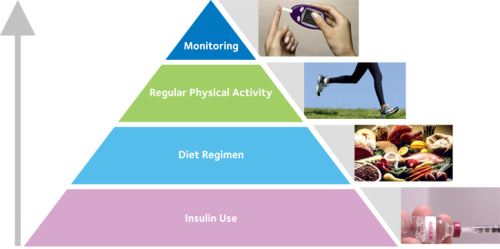
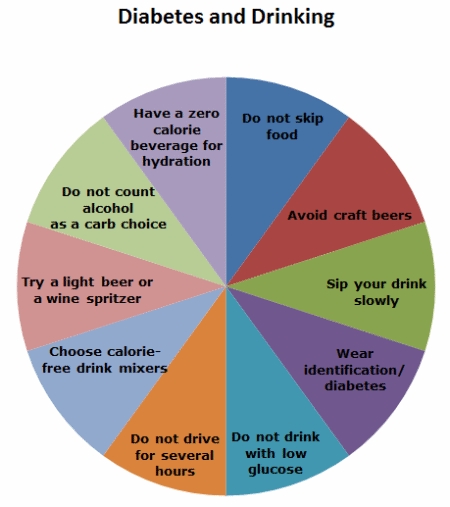
It is extremely essential to control the levels of blood sugar in pregnant mothers o as to prevent the complications associated with Gestational Diabetes [2]. The first and foremost step in the successful controlling of the conditions is to closely monitor the sugar levels in the bloodstream of the pregnant woman. This is recommended to be done several times a day and any unexpected change in the levels of glucose in the blood should be attended to at the earliest. While monitoring can be done at a professional healthcare clinic, it is highly recommended that pregnant mothers should monitor their blood sugar levels on their own as well. The process of monitoring is a relatively easy process and it can easily be made into a habit to last throughout pregnancy.

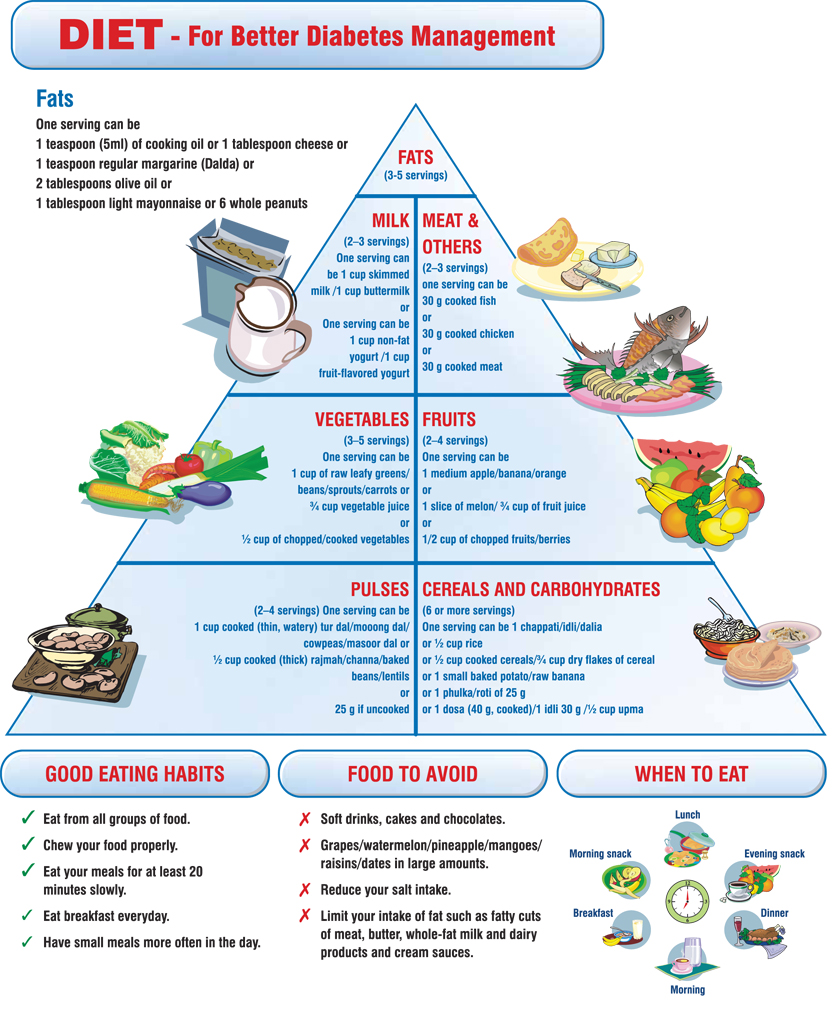
A healthy diet is the next step that a pregnant women suffering from Gestational Diabetes should take. The diet of a diabetic mother must have a correct balance of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, along with sufficient amount of vitamins, minerals, and calories. It is necessary to keep the glucose levels stable, and women should avoid skipping meals. Such women must avoid sugary items like candy, cakes, and aerated sodas. Recommended foods for diabetic mothers include having more of whole grains, fiber and also fruits and vegetables. Since all women have a unique physiology, their diabetic diet will differ from others. It is essential that a diet is based making all possible considerations and also in consultation with a dietician or a practicing healthcare professional.
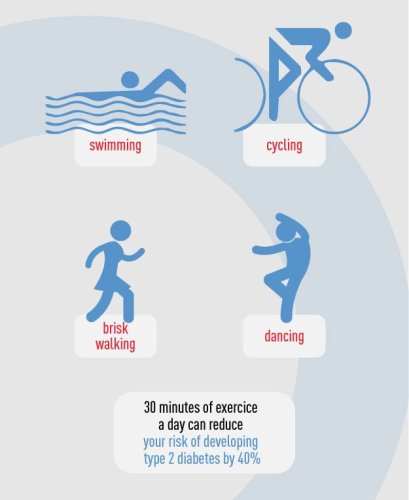
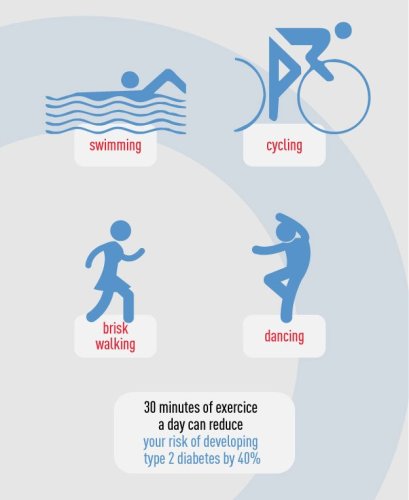
While exercise is recommended to everybody, it is an absolute must for diabetic mothers. Regular and frequent exercise promotes the cells of a diabetic to absorb the blood sugar more efficiently and this can greatly help in controlling the symptoms of Gestational Diabetes. Exercise also increases the sensitivity of the body to the released insulin. It is recommended that diabetic pregnant women should get as much moderate to rigorous exercise in a day as possible, after consulting a physician and a dietician.

In some cases, just exercising and maintaining a healthy diet are not enough in controlling the symptoms of the disorder and in such situations medications are required in order to help return the blood sugar levels to normal. Only 15% of women with Gestational Diabetes need medications like oral hypoglycemics or sometimes insulin analogues.
Regular monitoring of the blood sugar levels of both the mother and also baby will need to be carried out. There may be complications with the baby after birth and these will need to be attended to at the earliest. The monitoring of blood sugar levels will need to be continued throughout the lives of both the mother and the child as they stand a risk to developing diabetes later on in life.
Preparing for a Medical Appointment
In most common cases of Gestational Diabetes, the disorder will be diagnosed in the screening tests carried out in the third trimester of pregnancy [3]. Once diagnosed, diabetics will need to prepare themselves both physically as well as psychologically in order to combat the disorder. While this can be stressful, it must be remembered that the condition is life threatening and intensive care must be provided in order to protect the health of both the mother and the child.
Any medications that are being used by the diabetic individual should be disclosed with a physician to determine whether they can be continued or not. Any type of unusual symptom that the pregnant woman experiences should also be referred to the medical professional and all key personal information, including family medical history should also be made available to the physician.

It is also recommended that pregnant women who are diabetics have a close friend or an aide, who can help out in case the sufferer forgets or misses anything.
The different screening tests for gestational diabetes as also various other tests that are carried out over the course of treatment of the disorder are important and should be done properly. Some of these tests require fasting while others challenge the body’s ability to take up insulin and every test must be done as per the prerequisite that it has along with it.
There are also a number of support groups for diabetics and pregnant diabetic mothers can also try being a part of these groups [4]. Not only does this help in keeping sufferers cheerful, but it also helps sufferers gain a lot of knowledge as well as support from other people who are facing the same conditions. It is also recommended that women find out as much about the disease, its scope, the limitations of treatment and also future risks associated with Gestational Diabetes.
References
[1] Perinatal outcomes associated with the diagnosis of gestational diabetes made by the international association of the diabetes and pregnancy study groups criteria, Ethridge JK Jr, Catalano PM, Waters TP.; 124(3):571-8 – Sep 2014 – DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000412, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25162258
[2] Benefits and harms of treating gestational diabetes mellitus, Hartling L, Dryden DM, Guthrie A, Muise M, Vandermeer B, Donovan L.; 159(2):123-9 – Jul 16, 2013 – DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-159-2-201307160-00661, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23712381
[3] Screening and diagnosing gestational diabetes mellitus, Hartling L, Dryden DM, Guthrie A, Muise M, Vandermeer B, Aktary WM, Pasichnyk D, Seida JC, Donovan L.; (210):1-327 – Oct 2012: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24423035
[4] Epidemiological analysis of outcomes of pregnancy in gestational diabetic mothers, L. Martínez-Frías, E. Bermejo, E. Rodríguez-Pinilla, L. Prieto and J.L. Frías; – 6 DEC 1998 – DOI: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980630)78:2<140::AID-AJMG8>3.0.CO;2-S, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980630)78:2%3C140::AID-AJMG8%3E3.0.CO;2-S/abstract
[5] Gestational Diabetes and the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes, Catherine Kim, MD, MPH1, Katherine M. Newton, PHD2 and Robert H. Knopp, MD3; vol. 25 no. 10 1862-1868 – October 2002 – DOI: 10.2337/diacare.25.10.1862, http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/25/10/1862.full