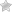There are a number of risk factors for diabetes which include dietary habits, obesity, physical inactivity, hypertension, genetic susceptibility, certain diseases or syndromes and other environmental factors that determine the chances of developing diabetes in an individual [1]. It is important to keep them in account and undergo regular blood sugar monitoring to prevent the development of diabetes at any stage of life.

Diabetes Diet
The first and foremost step to prevent diabetes is to have control over diet to prevent the risk of developing Type II Diabetes or may follow a diabetes diet [2]. The American Diabetes Association has made few recommendations in October 2013 for preventing and controlling diabetes. It states:
- Diabetics should avoid or limit the consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages especially those with caloric sweeteners like sucrose or high fructose containing a sugar that occurs naturally in fruits and honey. Fructose has 4 calories per gram. Corn syrup should be used to avoid any weight gain that may lead to worsening of cardiovascular risks.
- The general population should reduce sodium intake to less than 2300 mg per day which is also applicable for diabetic patients, with even more reductions for the ones with high blood pressure.
- The consumption of omega-3 supplements EPA or DHA for the preventing or treating cardiovascular disease is not of much use to the diabetic patients disease of the heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries).. Instead it is recommended to take at least 2 servings of fatty fish or at least 2 times per week for the general public and is also appropriate for diabetic people.
- It is also stated that there are no clear evidence of benefits from mineral or vitamin supplements for diabetics without any underlying mineral or vitamin deficiency. There is no evidence to support that the use of cinnamon or other herbs or supplements are effective for the treatment of diabetes.
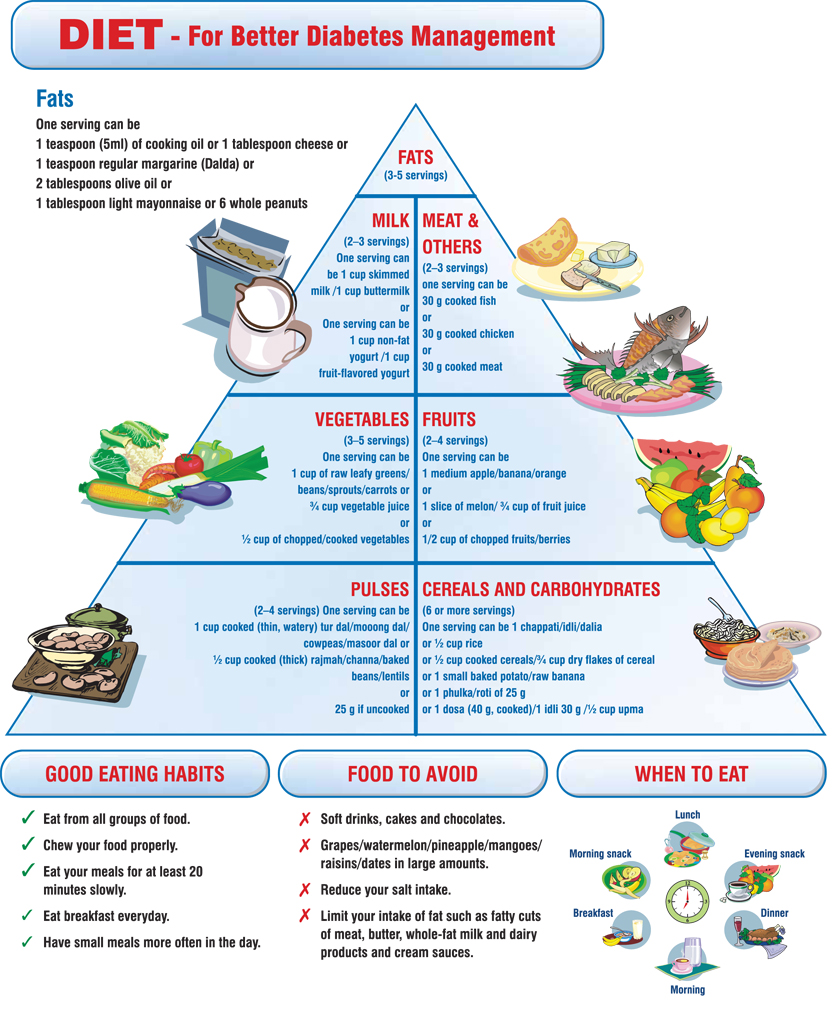
Tips for Diabetic Diets
The first and foremost tip regarding a diabetic diet is to choose slow releasing carbohydrates which are high in fiber. The following foods are considered to be high in fiber and slow releasing in carbohydrates:
- Brown rice or white rice which can be used in place of white rice
- Yams, sweet potatoes, cauliflower mash and winter mash should be used in place of white potatoes
- Whole wheat type of pasta should be used instead of regular pasta
- Whole grain and whole wheat bread should be used instead of white bread
- High fiber breakfast cereals should be used instead of sugary breakfast cereals
- Rolled oats or steel cut oats should be used in place of instant oatmeal
- Cornflakes should be replaced with bran flakes
- Corn should be avoided and instead leafy greens and peas should be used
Foods which have a low glycemic level should be resorted to as these foods are slow to be digested and sugar is released at a much slower rate than otherwise [3]. Some of the principles to be followed in order to follow low glycemic eating include:
- Eating a lot of foods which are low in starch such as fruits, beans and vegetables
- Only grains which have undergone lesser amount of processing should be eaten
- Refined grain products and white potatoes should be avoided as far as possible
- Concentrated sweets should be limited as far as possible
- Healthy protein found in fish, legumes and beans should be consumed
- Foods which have healthy fats such as nuts and olive oil can be consumed
- Full meals should be had throughout the day and snacks should also be consumed every day
- Meals should be had slowly and stopped when full
Food can be classified to lie in three different categories as per their glycemic indexes. These include:
- Fire foods: These foods have a high glycemic index and are low in protein and fiber. These foods should be avoided as far as possible. Examples of fire foods include white foods such as white pasta, white rice, sweets, fries and chips, processed foods, potatoes, white bread and baked food goods.
- Water foods: These foods are considered to be neutral and diabetics can have as much of these foods as they feel like. Such foods include only fresh fruits and vegetables and not any processed forms or even juices.
- Coal foods: These foods are low in their glycemic index and are high in both protein and fiber. These should replace all fire foods in a diabetic’s diet. Examples of coal foods include legumes, seeds, nuts, sea food, lean types of meat, whole wheat pasta, brown rice and whole wheat bread.

These days, all nutritional information with regards to manufactured or packaged foods is provided and diabetics must take care to ensure that they choose only those foods that have a low glycemic index. This will need to be done and if adhered to properly, diabetics can still follow a healthy life. It will enable diabetics to fell fuller for longer periods of time, while also reducing the blood sugar concentration by being digested much slower than other foods.
Processed foods and packaged cereal should be avoided and in general, the consumption of refined carbohydrates should be reduced as much as possible. Fruit juices should also be replaced with freshly cut or whole fruits as far as possible.
The second tip with regards to a diabetic diet includes being smart about the way sugary foods are handled. It is not necessary to completely eliminate sugar but the consumption of sugar should be limited and diabetics should be smart about handling such foods. Some tips that allow diabetics to include some of their favorite treats include:
- If dessert is wanted, then other forms of carbohydrates should be avoided. This keeps the extra carbohydrates in check.
- Desserts which contain healthy fat may be included in the diet as these are slow to be digested.
- If a sweet is to be consumed, it should be had along with a meal and not on its own. This lowers the rate at which sugar is released into the blood stream.
- If anything can be sweetened, diabetics should do so by themselves rather than accept other people’s measure of sugar. This can allow them to enjoy their food while keeping the sugar level in control.
- Soft drinks, juices and sodas will need to be reduced as far as possible from a diet.
- There are many fruits and low fat frozen yogurt options that can be used to replace ice creams and other unhealthy desserts. Dark chocolate can be had as opposed to milk chocolate.
- The dessert of a diabetic should ideally be half of that of a normal person and the other half should comprise of healthy fruits.

Consumption of alcohol should be handled with extreme care. Both the alcohol, as well as the mixers used in the drink can upset the calorie count in a diet. It is recommended that women have no more than a single drink and men have no more than two drinks a day.
Unhealthy fats should be replaced as far as possible with healthy fats [4]. Unsaturated fats, which are obtained from fish and plants, are considered to be the healthiest of fats and these should be used to replace the sources of unhealthy fat. Omega 3 fatty acids as found in salmon and some other fish are excellent sources of healthy fat. Some of the ways to reduce unhealthy fat include:
- Cooking with healthy oil such as olive oil instead of the traditional butter or vegetable oils
- Visible fat should be removed from meat as also the skin from the meat before cooking starts
- Seeds and nuts can be used as snacks instead of fries and chips
- Baked, boiled and grilled foods should be preferred over fried foods
- Fish should replace red meat as far as possible
- Avocado can be used as a healthy substitute to cheese
- Applesauce or canola oil can be used for baking rather than butter
- Low fat dairy products should be used in place of cream as far as possible
A diabetic must ensure that food habits are consistent and regular. Meals should never be skipped and it is often recommended that diabetics have up to six meals every day, keeping the calorie intake the same throughout each day. A food diary can also be used to help this purpose.
Myths about a Diabetic Diet
There are many myths that commonly surround diabetic diets. These include the following:
- Sugar must be avoided at all costs: This is one of the most commonly heard of myths which is quite far from the truth. If combined with a healthy exercise regime and a properly followed diet, with careful planning, a treat can be enjoyed, but only rarely.
- A high protein diet should be followed: This is quite contrary to the truth. Too much protein in the diet, especially animal protein can prove to cause resistance to insulin to be developed in the body and this is a key factor to the worsening of diabetes. The diet should be balanced and not protein concentrated.
- Diabetic foods will be needed: There are many branded supplements and special foods marketed as diabetic foods. These provide no additional benefits and also prove to be expensive. An old fashioned diet consisting of fresh fruits, vegetables and whole grains, with the appropriate balance of nutrients is good enough to keep the symptoms of diabetes in check.
- Carbohydrates will need to be cut down: While this is true to some extent, the key to a diabetic diet is to maintain a healthy and balanced diet which contains a mix of fats, proteins and carbohydrates in appropriate proportions.
Diabetes Prevention
Type I Diabetes unfortunately, cannot be prevented. The condition can only be controlled so that the diabetic patient can lead a normal life. This can be done by adopting healthy lifestyle choices and by maintaining a strict diet. Such sufferers of Type I Diabetes will need to carefully monitor and choose their actions throughout the course of their lives.

Besides diet, other factors necessary for prevention of Type II Diabetes, Prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes are [5]:
- Regular physical activities: It is important for people susceptible with diabetes to take up physical activities regularly to prevent or control diabetes. Physical activity helps to lose weight and lowers blood sugar by increasing blood circulation and adding to the responsiveness of insulin. This means that the body cells are able to accept the inflow of sugar more easily and consequently, the glucose levels in the blood are lowered.
- Losing weight: Losing weight and burning calories is must for reducing the risk of diabetes. One can start with mild exercise or even brisk walking to proper fitness training to reduce susceptibility to diabetes. Various studies have proved that there is up to 60% reduction in risk to develop diabetes in people who have lost over 7% of their body weight.
- Plenty of water consumption: It is also recommended to consume plenty of water to make up for the loss by urination. This also helps individuals keep themselves hydrated.
- Consuming more fibers: Consuming fibrous diet including fruits, leafy vegetables, whole grains potentially lowers the risk of developing diabetes by keeping healthy and also keeps away other heart related diseases. These foods can help people full for longer while providing much lower calories.
- Regular blood tests: Regular health check-up especially blood tests is a must now days to keep a check on the blood sugar status and timely prevention of developing diabetes. While this is recommended for everybody, people who face the risk factors of diabetes should definitely make sure to undergo these tests.
- Avoiding soft drinks and other beverages which contain artificial sweeteners. These artificial sweeteners are high in calorie content and can cause the normal blood sugar level to increase.
- In some special cases of prediabetes, oral medications such as Glucophage, metformin, Glumetza and many others may be used in order to prevent the onset of Type II Diabetes.
References
[1] Nutrition Recommendations and Interventions for Diabetes, Bantle, John Pand Wylie-Rosett, Judith and Albright, Ann L and Apovian, Caroline M and Clark, Nathaniel Gand Franz, Marion J and Hoogwerf, Byron J and Lichtenstein, Alice H and Mayer-Davis, Elizabeth andMooradian, Arshag D and Wheeler, Madelyn L.; 31 no. Supplement 1 S61-S78 – January 2008 – DOI: 10.2337/dc08-S061Diabetes Care, http://health-equity.pitt.edu/2864/
[2] Diet, nutrition and the prevention of type 2 diabetes, NP Steyna1 c1, J Manna2, PH Bennetta3, N Templea4, P Zimmeta5, J Tuomilehtoa6, J Lindströma6 and A Louheranta.; Volume 7 / Issue 1a /, pp 147-165 – February 2004 – DOI: 10.1079/PHN2003586, http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=569860&fileId=s1368980004000187
[3] Type 2 diabetes is prevalent and poorly controlled among Hispanic elders of Caribbean origin, Tucker KL,Bermudez OI, Castaneda C .; 90(8):1288-1293 – August, 2000 – DOI: 2105/AJPH.90.8.1288, http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/10937011
[4] Eating disorders in young women with type 1 diabetes. Prevalence, problems and prevention, Daneman D,Olmsted M, Rydall A, Maharaj S, Rodin G.; Suppl 1:79-86 – October, 1998 – DOI: 1159/000053110, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9677005
[5] Translating the Diabetes Prevention Program into the Community: The DEPLOY Pilot Study, Ronald T. Ackermann, MD, MPH, , Emily A. Finch, MA,; Volume 35, Issue 4 Pages 357–363 – October 2008 – DOI: 10.1016/j.amepre.2008.06.035, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0749379708006041