Today medications have become a common form of treatment for diabetes with a wide variety of medicines available all over the world [1]. It is still important to remember that medications are only part of the entire treatment program and a healthy diet with a lot of active exercise is essential for successfully controlling the symptoms of the diabetes. Nevertheless, medications can prove to be great in helping lower the blood sugar levels and to provide relief to diabetics.
Medications for diabetes include both oral tablets as well as injectable insulin for better and faster cure [2]. The purposes of diabetic medications include:
- To increase the production of insulin in the body of a patient
- To reduce the blood glucose levels in the body
- To decrease the absorption of carbohydrates from the alimentary canal
- To increase or to correct the response of the body cells to insulin
- To facilitate slower emptying of the stomach and the delayed absorption of carbohydrates
Medications for Type I Diabetes
Since Type I Diabetes is also known as insulin-dependent diabetes, the insulin is the major requisite in such patients. Since the body cells are unable to produce insulin internally, thus external insulin is administered which may be in form synthetic insulin or insulin analogues. These analogues are of two kinds:
- Rapid acting insulin analogues: Insulin Lispro, insulin Aspart and insulin Glulisine are some common rapid acting insulin analogues that are administered within 5-10 minutes of food intake and have rapid but short term effect. These are given in cases of high blood sugars to avoid any immediate increase in blood glucose level at the time of meals. The peak period of action is 60-120 minutes and the action lasts for not more than 4 hours.
- Long acting insulin analogue: Insulin Glargin and insulin Determir are long acting insulin analogues that do not have any peak action period and lasts for long once the drug is administered inside the body. The onset of action occurs 60-90 minutes after injecting and lasts for 12-24 hours. However, even for gestational diabetes, these insulin analogues are an effective cure.
Intermediate insulin administration options are also available for the administration of insulin to Type I Diabetes patients. This insulin may be injected intravenously into the blood stream or an insulin pump may also be used to administer insulin.

Some of the common insulin brands include Humulin, Novolin, Apidra, Levemir, Lantus, Humalog and Novalog [3].
Some other medications that are commonly used in Type I Diabetes cases include the following:
- An injection of symlin or pramlintide may be used to slow down the digestion of food to reduce blood sugar levels
- Medications to control high blood pressure may be often prescribed to reduce the risk of diseases
- Aspirin may be recommended in order to protect the heart
- Many cholesterol lowering drugs may be used in order to keep levels in check
Some emerging options for the treatment of Type I Diabetes include:
- Artificial pancreas: This process links a glucose monitor to an insulin pump which is in turn delivered to the body when there is a need to. The first step towards this procedure was approved in 2013 and the process has been receiving a lot of interest and active research is continually being carried out.
- Pancreas transplant: This process is not usually recommended as it involves high chances of risk of infection and many other side effects as well. This process is only carried out if any other organ of the body has failed and requires a transplant as well.
- Islet Cells transplant: The islet cells are the beta cells which are directly responsible for the production of insulin and these exhibit dysfunction in Type I Diabetes sufferers. Transplantation of the cells in order to infuse healthy cells that not only provide insulin, but also grow and multiply is used. However, this method is not widespread and has received little recognition due to the lack of healthy islet cells to be transplanted in comparison to the large number of diabetic individuals.
- Stem cell transplant: This is another newly sought after and emerging method of transplantation which might help Type I Diabetes sufferers. Stem cell transplants from a patient’s own blood can help the immune system to shut down and restart to function normally.
Other lifestyle changes and methods that can help in the treatment of Type I Diabetes includes following procedures including:
- Monitoring of the levels of blood sugars on a frequent basis
- Counting the carbohydrates consumption in the diet
- Maintaining a healthy and a well-balanced diet
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Getting lots of exercise
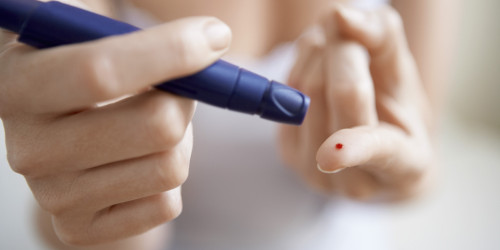
Medications for Type II Diabetes
There are several oral medications available for Type II Diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes to increase body’s response to insulin and regulate the blood sugar levels [4]. There are more than 18 types of drugs available in the market nowadays. These oral hypoglycemic drugs include:
- Alpha glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs) – These drugs help in slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates. An example of this class of drugs is Glucobay which is also known as Acarbose and greatly slows down the carbohydrate digestion process.
- Amylin agonists – Examples of this type of medication include Symlin or pramlintide that assist insulin in controlling post-meal glucose levels.
- Biguanidecs – These drugs prevents glucose production by the liver. Metformin is a common drug which can also help in increasing the sensitivity of the tissues of the body to insulin. Examples of biguanides include Glumetza and Glucophage. Some of the possible side effects that may be caused by this class of drugs include diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
- Gliptins or DPP-4 inhibitors – These medications prevent the destruction of Incretin hormones but have very small effect on reducing the levels of blood sugar. Examples of this class of medication include Tradjenta, Januvia, Onglyza, Sitagliptin, Vildagliptin and Saxagliptin.
- Megalintides – Similar to Sulphonylureas, these drugs help the body to produce more insulin but prove to be much faster acting and have a shorter lasting effect on the body. Possible side effects of megalintides include extremely low blood sugar levels and excessive gain of weight. Examples of megalintide drugs include Starlix and Prandin.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists or Incretin mimetic – These medications tend to mimic the actions of body’s Incretin hormone, but have very humble effect in reducing the blood sugar levels. Examples of this class of drugs include Victoza and Byetta.
- Thiazolidinedione or glitazones – These medications reduces the resistance of the body to insulin. However, this class of drugs is known to be associated with a number of side effects, including a higher risk of developing fractures and also failure of the heart. Examples of this class of medication include Actos and Avandia.
- Sulphonylureas – These drugs stimulate the insulin production by the pancreas. Common examples of Sulphonylureas include Glynase, DiaBeta, Glucotrol and Amaryl. However, possible side effects of Sulphonylureas include gaining of weight and very low blood sugar levels.
- SGL T2 inhibitors or gliflozins – These drugs lowers the blood glucose levels by acting on the kidneys and preventing them from reabsorbing the sugar back into the blood stream. The excess sugar is excreted out through the urine. Examples of this class of drugs include Farxiga and Invokana.
- Glinides or prandial glucose regulators – Prandin, also known as Repaglinide stimulates beta cells in pancreas to produce insulin and may be used to help Type II Diabetes sufferers.
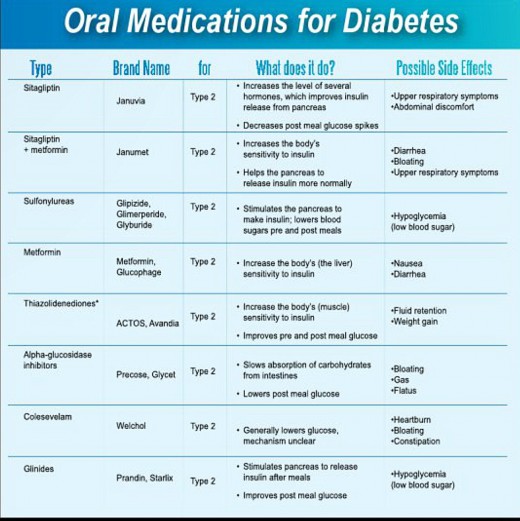
Insulin therapy may also be administered to Type II Diabetes patients in case of requirements. Insulin always needs to be administered externally and not orally as the enzymes present in the human stomach prove to interfere with the hormone. Insulin drugs may be administered either using an insulin pump or an insulin injection.
The common types of insulin therapy include the following types of options:
- Insulin Glulisine or Insulin Apidra
- Insulin Lispro or Insulin Humalog
- Insulin Glargine or Insulin Lantus
- Insulin Aspart or Insulin Novalog
- Insulin Isophane or Insulin Humulin and Insulin Novolin
- Insulin Determir or Insulin Levemir
Besides treating Type II Diabetes, these drugs are also used in the treatment of two other types of diabetes, namely Gestational Diabetes and prediabetes. However, the use of medications is rarer in these cases and very often; only healthy lifestyle changes, active physical exercise and a diabetic diet can prove to be enough to help control prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes.
There are a few precautions needed before going for these drugs and analogues for treatment of diabetes:
- The type of diabetes: While the symptoms and the conditions of Type I and Type II diabetes may appear to be the same, care must be taken to correctly identify the type of diabetes before beginning taking medication. The two types of diabetes are known to have very different causes and as such, their treatment procedures and medications are quite different.
- The cause and magnitude of diabetes: While the chronic conditions may exhibit extremely high blood sugar levels, lower levels can be controlled by following a healthy diet and maintaining an active lifestyle with adequate amounts of exercise. This more often than not proves to help control the symptoms in less severe cases and also in prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes.
- The adverse effects and drug reactions: Most of the drugs that are used in the treatment of different types of diabetes are known to have different types of side effects on the body and in case medications are being taken, then these side effects will have to be managed.
- Other medical conditions: Conditions like hypertension, thyroid etc. which may co-exist with diabetes can cause interference with the medications for diabetes. This can cause a lot of complications and can be potentially hazardous. Other associated diseases and any underlying and latent diseases will need to be thoroughly sought for before the medication for diabetes can be prescribed to full effect.
- Compliance factors: There may be a host of compliance factors associated with different types of drugs as per the location of a user. Care must be taken that if a person is required to travel or relocate, the medication is available to be used in all locations visited. This can be a hassle as different countries have different agencies that approve the drugs to be sold and used.
- Contradictions to therapy: While different drugs have proven to be effective in their own ways, there have also been a number of cases involving contradictions to the type of therapy used. As such, any medication should always be resorted to only after the recommendation of a licensed medical professional.
- Cost effectiveness of the treatment procedure: Different treatment procedures have different costs and it is up to the patient to determine which process is financially feasible. Fortunately, many healthcare providers and diabetic clinics offer consultation to help suffers avail the right kind of treatment as per their lifestyle and budget.
It must be remembered that there is no treatment or cure for diabetes and any condition of diabetes should be considered serious. While the symptoms of the disorder can be controlled to some extent with the help of regular exercise, physical activity and by following a diabetic diet, sometimes the use of medication cannot be avoided. Even in such cases, the physical activity and the diet must continue throughout the life of the diabetic.
It is critical that diabetics always seek proper medical counseling and advice from licensed medical practitioners or healthcare providers before deciding to take up any type of medication [5]. All types of medication are known to be associated with their own sets of hassles and side effects and diabetics will need to effectively manage living with these mild side effects and also will need to mentally prepare themselves to battle the disorder throughout the entirety of their lives. There is a lot of active scientific as well as medical research being carried out in order to find a permanent cure for diabetes. Till then, all types of diabetic sufferers including those suffering from prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes will have to be hopeful and continue following a strict diet and a healthy lifestyle.
References
[1] Glycemic Control From 1988 to 2000 Among U.S. Adults Diagnosed With Type 2 Diabetes, Carol E. Koro, PHD12, Steven J. Bowlin, DO, PHD1, Nancy Bourgeois, BS1 and Donald O. Fedder, DPH2.; vol. 27 no. 1 17-20 – January 2004 – DOI: 10.2337/diacare.27.1.17Diabetes Care, http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/27/1/17.short
[2] Trends in Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension in the United States, Ihab Hajjar, MD, MS; Theodore A. Kotchen, MD.;;290(2):199-206 – May, 2003 – DOI: 11001/jama.290.2.199, http://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?articleid=196894
[3] REDUCTION IN THE INCIDENCE OF TYPE 2 DIABETES WITH LIFESTYLE INTERVENTION OR METFORMIN, N Engl J Med.; 346(6): 393–403 – 2002 Feb 7 – DOI: 1056/NEJMoa012512, http://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa012512
[4] Predictors of medication nonadherence among patients with diabetes in Medicare Part D programs: A retrospective cohort study, Noel E. Wilkin, RPh, PhD, William B. Lobb, RPh, PhD.; Volume 31, Issue 10 Pages 2178–2188 – October 2009 – DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.10.002, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19922889
Bedienungsanleitung.
[5] Effects of Intensive Blood-Pressure Control in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, The ACCORD Study Group,; 362(17): 1575–1585 – Apr 29, 2010 – DOI: 11056/NEJMoa1001286 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4123215/